VERYSchool¶
Valuable EneRgY for a smart School
– Project web-site – Contact –  –
– ![]()
Pilot Sites – Approach – Impact – Exploitation – Conclusions and Recommendations – Partners
VERYSchool was a result-oriented, an industry led and market driven project co-funded by the European Commission (GA number: 297313) as Pilot actions under the Competitiveness and Innovation Programme (CIP-ICT-PSP 2011). The Energy Action Navigator, called VSNavigator, was the core development to deploy innovation for energy efficiency in school buildings.
VERYSchool Efficiency is here intended as a process that optimises the Energy Management System, during decisions phases, future planning, current management, correction of the on-going operational program. All these phases always complying with the practices of the ISO 50001 International Standard. Focusing on Pilot activities, VSNavigator and the VERYSchool project as well, has been demonstrated and validated through one year of real-size field tests, measurement and feedbacks for improvements. The entire project helped to promote, guide, disseminate and raise awareness in school organisation, with the new technology, VSNavigator, as focal point to understand how schools currently manage their energy programs, how they identify possible barriers, how they promote opportunities and share best practices. It is to underline that any reference to the school building, or school organization, automatically extends to the general concept of “building” or “organisation”.
Pilot Sites¶
The VERYSchool project engaged four Pilot Schools, located in Italy (Lesa and Genoa), Bulgaria (Plovdiv) and in Portugal (Lisbon). The ICT used in the project comprise, Bems hardware and software (with smart metering and smart LED lighting), Action Management and simulation suites.
Contents of the project ICT development have been supported by one year of real-size field tests and measurement with VSNavigator installed in the four Pilots. The local Bems operating in real-time, continuously transmitted, e.g. from Pilot to VSNavigator, the experimental data with a time frequency of 5 minutes. Therefore a consistent amount of experimental data have been collected and the database is made for public download to the benefit of the scientific Community at the link fpt:// ………………………. Experimental data monitoring was the initial key source of information to produce High Quality Data Set (HQDS). Aggregating the experimental data, HQDS has generated averaged: Quarterly data (15 minutes), Hourly data (60 minutes) and Daily data (24 hours).
The complete set includes also data not directly measured but calculated, such as thermal and lighting energy consumption for each room of the Pilot, also detailed for type of source, such as traditional lamps, LED with and without dimming control. Moreover, counters of events are also included to understand the current people behaviour and the rules of the existing action plan; typically, events such as “Bems operated in manual mode”, “Windows opened and Heating ON”, “Light ON without presence in the room”, “Indoor temperature higher than the set-point and Heating ON” are some representative examples.
Approach¶
VERYSchool was a result-oriented, an industry led and market driven project co-funded by the European Commission (GA number: 297313) as Pilot actions under the Competitiveness and Innovation Programme (CIP-ICT-PSP 2011). The Energy Action Navigator, called VSNavigator, was the core development to deploy innovation for energy efficiency in school buildings.
Efficiency is here intended as a process that optimizes the Energy Management System, during decisions phases, future planning, current management, correction of the on-going operational program. All these phases always complying with the practices of the ISO 50001 International Standard. Focusing on Pilot activities, VSNavigator and the VERYSchool project as well, has been demonstrated and validated through one year of real-size field tests, measurement and feedbacks for improvements. The entire project helped to promote, guide, disseminate and raise awareness in school organization, with the new technology, VSNavigator, as focal point to understand how schools currently manage their energy programs, how they identify possible barriers, how they promote opportunities and share best practices. It is to underline that any reference to the school building, or school organization, automatically extends to the general concept of “building” or “organization”.
Quality of the Consortium, EU dimension and social cohesion¶
The VERYSchool project have involved a cross section of people and organisations with expertise in the field of technology integration, energy management, public awareness and private end-users. Industries, R&D and SME offered qualified solutions on energy management and building control, promoted innovation and penetration of technologies and concepts. The two Regional Energy Agencies (AESS and EAP) established a link with local communities and took energy performances updated with current legal requirements. The Public Authorities (Municipality of Genoa and Ankara National Education Directorate) offered vision, leadership and help to shape policy development. The ESCO (EPRO) and the Bank consultant (ISPE) developed the financial aspects for understanding how schools currently finance their energy efficiency improvements, while they outlined how the financing options can change according to the model adopted.
Impact¶
VERYSchool has developed an Energy Management software platform, called the Energy Action Navigator, or simple VSNavigator, that has been customised for school stakeholders and that provides the tools necessary to develop and implement a systematic Energy Management Programme at organisational and building levels with respect to decision-making, energy policy and building operation. The soundness of concept and of the overall objective are depicted as “roadmap” and they are shown in the following figure.
The Client (schools and the associated stakeholders) were placed at the centre and ICT-related energy efficiency clusters have been built around the Client to support the realisation of energy efficiency and savings. In particular, the Energy Management Challenges addressed for schools focused on:
- How do achieve energy savings quickly?
- How do determine and prioritise energy saving measures?
- How do reduce energy cost at individual building and at many buildings (district)?
- How do reduce energy and costs, year after year?
Thus, the Clusters customised to the needs of schools and associated stakeholders include several hardware and software technologies (LED Lighting, Smart Meters), Building Energy Performance Software (simulation), building operation (Bems), renewable energy technologies, energy programs (Energy Action Management Software), standards (practice of ISO 5001), assessment methods (IPMVP), knowledge creation, and knowledge exploitation. VERYSchool have had both a technical and operational component. The project have integrated monitoring and targeting performances, smart and LED lighting, smart metering, energy simulation in support of school-specific energy optimisation scenarios. The operational component has been linked to VSNavigator and have provided stakeholders at all levels access and a way to manage optimisation scenarios and energy conservation measures for their facility.
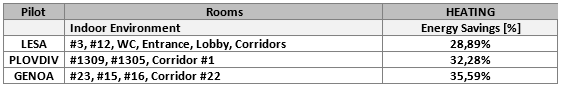
Energy Action Plan and Management System¶
A devoted Action Plan was adopted for matching the requirements of demonstrating and validating the VERYSchool project and VSNavigator as well. The following Optimisation Scenarios, from the Catalogue, were implemented. ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT - OS #13: Implement behavioural rules to save energy (remind turning off unused devices, close windows when HVAC system is on, etc.)
HEATING OS #21: Install an Outdoor Temperature Compensator for the Heating Unit; OS #22: Install thermostatic valves to radiators; OS #23: Install a zone heat metering system coupled with cost allocation system; OS #26: Replace the Heating Unit The OSs #21, #22 and #23 required investment costs that were covered within the project budget. The OS #26 refers only to PLOVDIV with costs covered by the school Organization, thus no charged in the project.
LIGTING OS #27: Increase lighting efficiency; OS #28: Set up occupancy based lighting control; OS #29: Set up dimming lighting control; OS #31: Split the electrical lighting circuits; All these OSs required investment costs that were covered within the project budget.
SYSTEM SETTING STRATEGIES OS #32: Optimize the thermostat set points during the day by keeping it at minimum allowed level (e.g. 21°C switch to 20°C); OS #33: Optimize the thermostat set points during unoccupancy of the school (trade-off between keeping at minimum level or switching the system off.); OS #35: Adjust timers to optimize switching “on” and “off” of the heating system before and after occupancy (Ramp Up); OS #36Implement a remote control of radiators (zoning by room), with calendar scheduling option;
RENEWABLES OS #55: Install a Photovoltaic (PV) system; OS #56: Improve the use of the PV system; The two OSs refers only to LESA with costs covered by the school Organization, thus no charged in the project.
MANAGEMENT-BEHAVIOR OS #64: Carry out lighting analysis; OS #65: Carry out HVAC analysis; OS #66: Carry out analysis of other electrical use and appliances; OS #68: Raise awareness of staff, pupils and school personnel; OS #70: Ensure lights are switched off at breaks and after school; OS #74:Communicate with Staff; OS #75: Communication for Students; OS #76: Monitoring of energy supply contracts including global service contract
Energy and Environmental Challenges¶
The energy and environmental challenges that the VERYSchool project pursued along its three year of technical development, demonstration and validation, were established on several levels levels.
- Building Energy Index (BEI) and Climate Energy Index (CEI)
- Energy assessment using KPIs
- Energy Flow Assessor
- Carbon Assessor
- IPMVP customized for school environments
- eeMeasure
Building Energy Index (BEI) and Climate Energy Index (CEI)¶
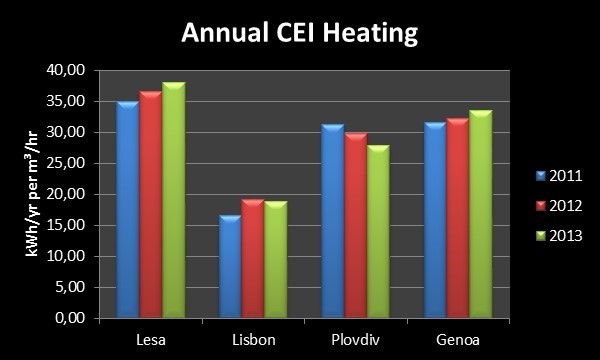
The Building Energy Index (BEI), embedding the Climate Energy Index (CEI), is a tool of the IES <VE> suite, used to consider any worldwide climate for the purposes of sustainable buildings at both design and operational phase. Climate underlies building energy use; it is therefore necessary to evaluate building design and performances versus climate, to highlight where emphasis needs to be placed while directly and interactively tracking the effect of design strategies. The BEI was adapted to the VERYSchool project, by first calculating the CEI for each pilot location, before feeding into the BEI assessment. The CEI is the energy required to take a flow rate of one m3 of air per hour within a defined comfort zone. As heating is the only space conditioning end-use common for the four pilot schools in the project, CEI Heating values were produced for the four locations of GENOA, LESA, LISBON, and PLOVDIV based on simulation weather data over the period 01/01/2011 to 31/12/2013. The chart below shows that the LESA location has the highest CEI heating value, and hence the highest heating burden imposed upon the building. Plovdiv and Genoa both display similar annual total CEI Heating values. By far LISBON displays the lowest CEI Heating value, and hence there is no heating at this pilot location.
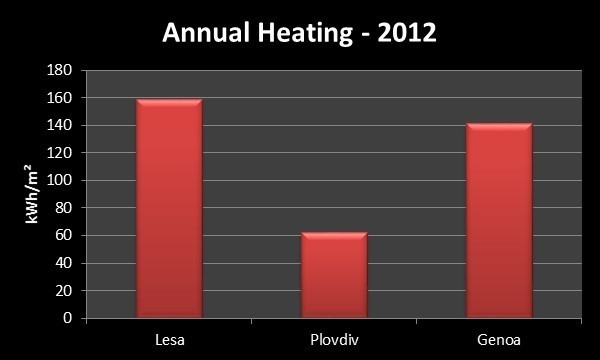
Through the BEI, the energy consumption of the pilot building as a function of the climatic burden (CEI) was then expressed. This allows for the comparison of heating energy in the different locations, taking into account differences in building size and occupancy hours also. The BEI formulated by dividing the Heating Energy through by the CEI value for each location times the building are shown in the figures below.
The results of this analysis show that, relative to their respective climatic burden, the buildings located in LESA and Genoa perform equally as effectively. Thus while LESA does consume more heating energy than GENOA this could be attributed to the colder weather conditions rather than it being as a result of poorer building performance. PLOVDIV by contrast shows much better performance than the other two sites relative to its climatic burden.
Energy assessment using KPIs¶
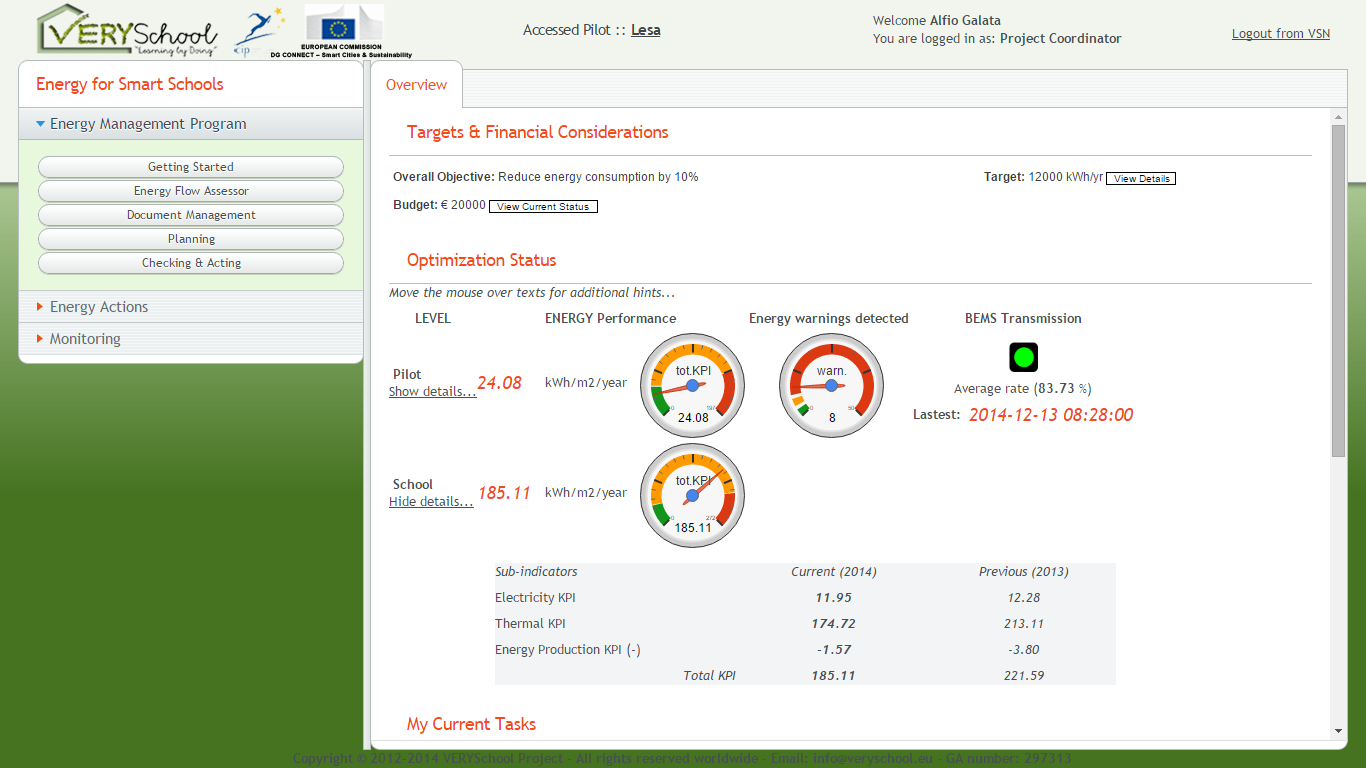
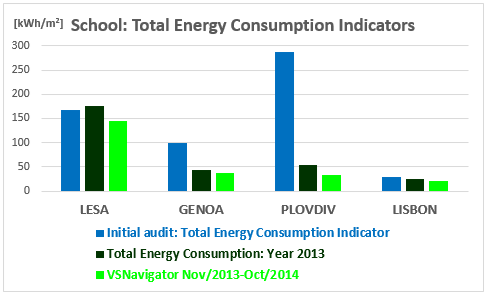
KPIs are part of the VSNavigator functionalities. They are calculated for both the School and the Pilot area on daily basis and compared to expected targets. They are displayed in the Start page of VSNavigator to highlight energy performances and the aim to create a real-time awareness on current energy behaviour. Figure below shows the performance in terms of total energy indicators [kWh/m2] achieved in each pilot school, in regards to:
- the VERYSchool measured energy consumption data during the one year (2014) of experimental campaign,
- the consumptions data of the previous year (2013), and
- the values calculated with the initial energy audit done at the beginning of the project to establish the baseline for the final evaluation.
Through VSNavigator, and the level of innovation introduced,
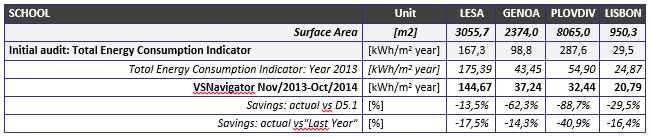
- the LESA school achieved savings of 17,5% versus the previous year and 13,5% versus the starting point of the project.
- the GENOA school achieved savings of 14,3% versus the previous year and 62,3% versus the starting point of the project.
- the PLOVDIV school achieved savings of 40,9% versus the previous year and 88,7% versus the starting point of the project (here is to be mentioned that the School changed the boiler at the beginning of 2013 to switch for coal to gas fuel generation system).
- the LISBON school achieved savings of 16,4% versus the previous year and 29,5% versus the starting point of the project.
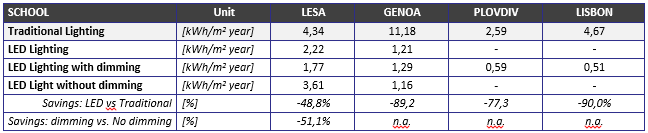
Moreover, as part of the final validation results, the efficiency of LED Lighting versus the traditional one has been assessed. Results are in the table below
The LESA school achieved savings of 48,8% for LED versus traditional lights, and 51,1% of dimming control versus the automatic ON/OFF control based on the room occupancy. The GENOA school achieved savings of 89,2% for LED versus traditional lights. The PLOVDIV school achieved savings of 77,3% for LED versus traditional lights. The LISBON school achieved savings of 90,0% for LED versus traditional lights. For GENOA, PLOVDIV and LISBON, the dimming control can’t be evaluated versus the automatic ON/OFF control based on the room occupancy because of the non-homogeneous characteristics of the rooms.
Energy Flow Assessor¶
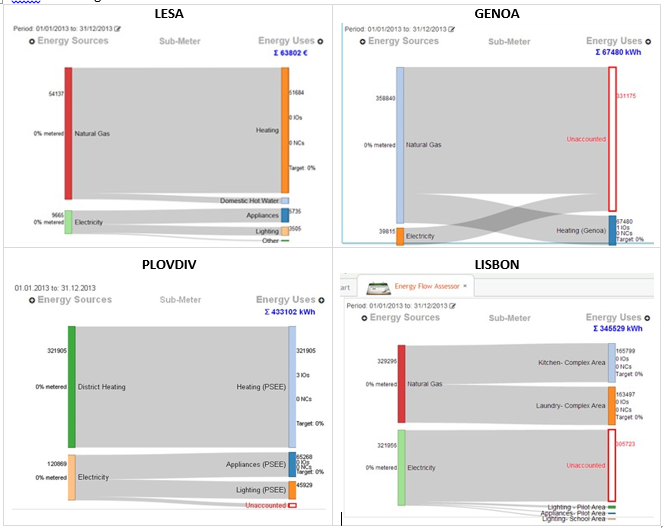
Energy Flow Assessor (EFA) is a tool of Enerit Action Management used to highlight the energy flows towards the final end-uses. The outcome is a diagram (graphical representation of the connections) that associates the energy sources (e.g. electricity, natural gas, etc.) used in the School with the different uses of these sources (e.g. heating, hot water, lighting, appliances, etc.), showing the relationship between energy sources and consumption at school level. Therefore, EFA is a crucial facility for Energy Planning and Energy review stage of implementing an energy management system since it represents a snapshot of how energy is actually used in the organization.
As an option, EFA displays the same outcomes in terms of energy costs for each source and end-use.
Carbon Assessor¶
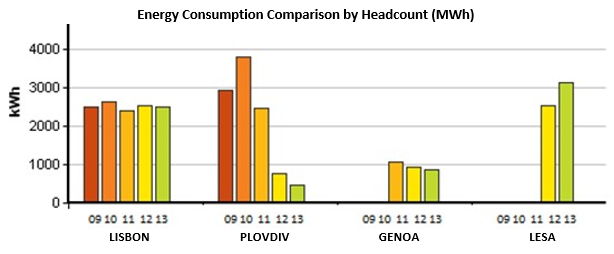
The Carbon Assessor tool is marked by IES to gather and analyse building energy data and to check compliance with the Carbon Reduction Commitment (CRC) energy efficiency scheme. The tool calculates overall building and portfolio energy use, carbon footprint and fuel costs and provides an indicative comparison of each buildings performance against the overall portfolio. Furthermore, it highlights areas of inefficient energy use and under-performing buildings to target reduction activity where it is most effective. In the VERYSchool project, Carbon Assessor has been employed as useful tool to establish a benchmark for the pilot Schools in relation to carbon emissions, energy consummation and resulting energy costs. The schools were benchmarked, over a period of 5 years, against each other for comparison under the same headings in relation to building, area and headcount.
The school pilot Carbon Assessment has been deployed as a result of the VERYSchool project.
IPMVP customised for school environments¶
IPVMP (International Performance Measurement and Verification Protocol) is considered as reference methodology to support performance-based contracts. It describes in 13 steps the standard procedures that, when implemented, allow building owners, decision makers, managers, ESCO, and Investors on energy efficiency projects (e.g. banks) to quantify the performance of energy conservation measures and related energy saving to evaluate the cost impact and financial options. Taking as reference the 13 IPMVP steps, the IPMVP customized for school buildings (e.g. the VERYSchool methodology) provides a reasonable understanding on how to calculate energy savings and assess indoor comfort in school environments. The key aspects of the VERYSchool methodology are summarized below.
Use of experimental dataset of limited time (both for baseline and post-retrofit periods) and limited number of rooms, both for lighting and for thermal consumptions.
- Consider as renovation actions those implemented in the project, that were:
- the installation of thermostatic valves on the radiator, in each room of the Pilot area, to perform the ON/OFF control (set-point ) of the indoor temperature;
- the installation of LED lighting in some rooms, and some LED with dimmers, to perform the ON/OFF (set-point) and dimming lighting control in these rooms.
Consider the “school scenarios” in the “real time execution” to refer to the operational Optimized Scenarios of VSNavigator, and in particular: (1) zoning programming, (2) thermostatic setpoint, (3) LED light, (4) control presence on lights and (5) dimming on lights.
The energy savings results on Heating consumption, mostly achieved due to the implementation of the Optimization Scenario #22: Install thermostatic valves to radiators, are summarized below.
The energy savings results on Lighting consumption, mostly achieved due to the combination of the implemented Optimization Scenario: OS #27: Increase lighting efficiency; - OS #28: Set up occupancy based lighting control; OS #29: Set up dimming lighting control; OS #31: Split the electrical lighting circuits are summarized below.
eeMeasure¶
Energy savings for the Energy Conservation Measure (Action Plan) implemented in the four Pilots have been assessed also by using eeMeasure software tool (provided by the EC to validate results of EC-CIP projects). This assessment provides a good understanding of energy savings achieved on thermal, and lighting end-use consumptions. Results of 6 case studies performed for one year period, show that:
- Installing radiator control valve on each heat emitter in 3 Pilot-schools with hydronic heating, energy saving around 30% has been achieved for thermal consumption;
- Measuring thermal consumption by heat meter in whole school (PLOVDIV) and Pilot area and the adjacent space (GENOA) where radiator control valves were installed only in the Pilot area and the other radiators have no local heat output control but only central, energy saving up to 10% has been noticed for heating consumption.
- A potential energy saving in the range from 60 to 90% is proved in 4 schools as convenience of LED lighting with dimming against traditional lamps
- In two schools (LESA and LISBON) a potential of energy saving between 16% to 40% is envisaged by comparing the LED lights with dimming control versus the ON/OFF lighting control (this achieved with the same electrical power and room in “very closed” living conditions and configurations).
- Comparing LED lights without dimming against traditional lamps in LESA Pilot for the period of one year, a potential energy saving of nearly 50% has been noticed.
- Automatic control of traditional lamps against manual ON/OFF control in two classrooms in PLOVDIV school achieved electricity saving of around 25% in the test period.
Contribution towards Near-Zero Energy Buildings¶
Based on the catalogue of the Optimisation Scenarios, a Green Design has been performed for each pilot, and RET strategies included, for demonstrating how the existing pilot schools can be transformed into Near-Zero Energy Building. Therefore, for each pilot a number of design and operational scenarios that suite for possible implementation on the existing infrastructure have been selected. Energy performance of these selected optimization scenarios have been assessed through simulations performed with the pilot calibrated models. The results allowed to determine the effect on energy usage and in turn carbon emissions and an attempt to achieve a net zero or positive building. The gain introduced by the whole set of selected Oss, in terms of individual energy saving performances have been greater than 100% when evaluated individually. Thus, a restricted set of scenarios has been finally proposed and the overall performances have been evaluated also versus capital costs and payback periods. The aims of these case studies would provide the decision-maker with all the information for a selective choice that allow to reach the nZEB targets. The majority of school building stock in EU have no RET technologies installed. Researches in the project have shown that schools which already use renewable energy sources, in most cases have either solar power plants for electricity generation (PV Plants), or thermo solar plants for producing thermal energy commonly for heating domestic hot water or water for the swimming pools. There are some cases where cogeneration, as the simultaneous production of electricity and heat (Combined Heat and Power or CHP) is applied. In some schools the fossil fuel boilers are replaced with biomass boilers, but there are very few examples where geothermal and especially wind energy is used in school buildings. The massive use of renewable energy coupled with effective energy management is the optimal mixture to reach Near-Zero Energy Targets.
Exploitation¶
Wider Societal Implications¶
Evaluating the impact and legacy of a project at the moment of completion is challenging because it involves assumptions about the future. There are however some clear indications that demonstrate very clearly that the work carried out in VERYSchool could have a positive legacy. With a new vision, innovative but mature thechnologies, Organization’s rules and user’s behaviour have been merged to be a whole and sole process driving the Energy Management System through the advanced technology solution provided by VSNavigator. VERYSchool has demonstrated under real operational conditions that can contribute directly to reduce energy consumptions in European schools. Supporting this outcome, the project validation has demonstrated that a substantive energy saving can be achieved in annual consumption; specifically for the four pilot schools of more than xxx% on average, that contribute to xxx% of carbon emissions reductions. The experimental data collected during one year of field tests and monitoring at the Pilot locations, as well as the High Quality Data Sets generated from the experimental data, are made for public and scientific use, to the benefit of the Community. Due to the nature and longevity of the VERYSchool project, the high level of technical solution and the cutting edge technology development, merged with a complete set of practical “how to” implement systematic energy management programs (learning by doing), provided the direction for sharing the knowledge and model for replicating customisable energy savings strategies and energy efficiency concepts in the European school building segment. Because the Consortium involved public authorities, energy agencies, ESCO, system integrators and technology providers, at the appropriate level (national, regional or local), and the project provided evidence of the timely usability of VSNavigator working in pilots the consistent methodology adopted for communicating and promoting objectives, outcomes and results, allowed to link with various stakeholders and users alike to collectively address the issue of energy management in schools. Dissemination and communication were a basic activity in the VERYSchool project, to create:
- awareness on the strategic role the energy management (and ISO 50001) has towards sustainability, low-carbon Society and near-zero energy buildings;
- the basic conditions so that other “interest groups”, e.g. other than those involved with schools, can take the objectives and findings of the VERYSchool project.
Several and differentiated communication channels and tools have been used to reach the target groups and the Community at large. Among these, the on-line survey that involved about 2.000 responders, provided information on the actual level of knowledge for implementing an Energy Management System in European schools (both, buildings and organizations). On the same time, this initiative created the foundations to directly share the modern concept the VERYSchool project is introducing through VSNavigator as efficient and powerful tool of a new generation of ICTs for Energy Efficiency and for the implementation of the ISO 50001. The project exploitation approach, and in particular the business model which includes detailed plans for sustainability and larger scale uptake beyond the project, provides socio economic evidence for ICT investments in the field, as well as user acceptance and recovery of investment. Furthermore, the deployment of VSNavigator as a product/solution, and the related services that can be built around, can be replicated for other building types and Organizations other than schools. This increases the potential for the creation of quality jobs and economic growth, especially among SMEs. Evaluating this impact of the project at the moment of completion is challenging because it involves assumptions about the future.
Targeted Users¶
Several people can be involved for the use of VSNavigator.
- Public Administration and Corporate Executives, who do not follow the technological evolution, and often are not interested in, are assisted in making decisions on cost effectiveness for energy renovations and guided in selecting the most profitable and environmentally sustainable solutions, where savings pays for investments.
- Operational Executives, including Energy and Facility Managers, are assisted in making decisions during the implementation of the Operational Program and guided in the choice of high efficiency solutions.
- Technicians are assisted in making effective the implementation of the operational program, according to the standard ISO 50001.
- ESCO, that promote business models based on the concepts of “green economy”, in which energy savings pays for investment.
- BMS technology providers, which jointly with their technological supply, are expanding the range of services including even the “energy performance contract”. These companies can take advantage of VSNavigator to overcome the limits of the existing SCADA.
Degree of innovation¶
VERYSchool received the first Green Digital Charter (GDC) Award, with the Ceremony held in Amsterdam on November 2013, during the NiCE roadshow (Eurocities 2013).
Finally, as a platform to engage stakeholders and to link them with and capture their interest towards the project, a “Networking” menu has been implemented in the project website, while the project is visible in Facebook and Linkedind Social Network.
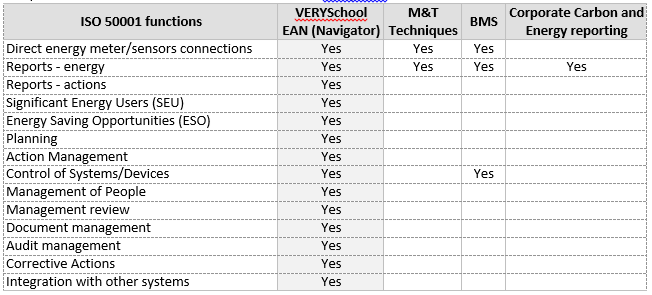
VSNavigator is a product for energy efficiency in school buildings technologically new. This innovative tool provides a quality improvement of existing solutions for Energy Management, since it introduces a repeatable integration of techniques and technologies with Monitoring & Targeting techniques (M&T), utility billing system, (semi-) automated billing entry, (semi-)automated reading entry. Using VSNavigator, Energy Management becomes a systematic methodology that comply with all the requirements of the ISO 50001 international standard. The PDCA cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act) governs the activities within the Organization, suiting with current management, correction of the on-going operational program, decision-making and future planning. The innovative and high technological level ensured by VSNavigator versus market product and actual compliance with ISO 50001 state-of-the-art solutions is depicted in the table below.
VSNavigator, putting Energy Management at the centre of its performance. is a replicable solution that can be extended to any type of Buildings or Organizations, not only to all schools, across Europe. The innovation in VSNavigator lead to a product which is superior to alternative solutions, while creating higher quality services. This innovation meets the same market opportunities than other, especially among the ESCO, that promote business models, in which energy savings needs to be accurately assessed and action plans agreed and documented to pays for investment. On the same time, VSNavigator forms a basis for the generation of new industries, since BMS technology providers, which jointly with their technological supply are expanding their business including even the energy performance contract, can take advantage of VSNavigator to overcome the limits of the existing SCADA. Furthermore, VSNavigator targets Public Administrator and Managing Directors, who do not follow the technological evolution and often are not interested in, Operating Executives, including Energy and Facility Managers and Technicians, in making decisions on cost effectiveness for energy renovations, and during the implementation of the Operational Program, making it effective according to the ISO 50001 standard.
Financing Energy Smart Schools¶
A Guide ‘’Financing Energy Smart Schools’ has been produced for publication. This guide aims to support decision makers in school looking for resources to implement their energy efficiency projects, identifies the available financing options (internal financing/debt financing /energy savings performance contracts), with a special attention to innovative instruments such as ‘Revolving Green Funds’ and to existing best practice in Europe and abroad.
VSNavigator has been developed with the contribution of European funds as CIP-ICT-PSP project, but it is also the result of a research and innovation action. Thus, the VSNavigator software is not released as a product ready for the market. The Consortium is aware to be not able to create any “spin-off company” or “joint-venture” after the end of the project. The VERYSchool Consortium only pursues the goal to give value to the efforts and the expenditures made with public money to strengthen the competitiveness and Innovation of the European Industry. Thus, to make the business plan realistic and successful, the Consortium set up an exploitation strategy that considers the “sell of the rights” of the VSNavigator software to Organizations who wish to buy. The long term viability of the product is addressed because VSNavigator is a solution that provides value for energy management, being on the same time friendly, manageable and low to no maintenance. The value added solution and the implementation at large are ensured by following the VSNavigator systematic approach, which:
- helps decision makers to fund parts of the energy management program through energy savings,
- allows decision makers to control the velocity of the program (e.g. timing of investments),
- changes the organizational culture through the implementation of an energy savings program.
Moreover, enlarging the long term viability concept, VSNavigator is a product that generates services and that can be implemented by parties acting alone or in consortium, upon agreements that provide the basis for joint value creation. The wider deployment and use, fitting with the objectives of the business model, is based on the assumption that VSNavigator is a:
- customised solution that addresses the unique needs of and the entire value chain of schools (e.g. city councils, public managers, energy managers, technicians, maintenance workers, global service, students and teachers);
- replicable solution because any reference to the school building, or school organization, automatically extends to the general concept of “building” or “organization”.
- competitive product with integrated award winning, leading, and cutting edge technologies.
According to the established business model, the Consortium is already prepared, organised, and has a network, especially among ESCOs, professionals and ICTs organisations that, buying VSNavigator, can exploit the product in its reference market.
Conclusions and Recommendations¶
VSNavigator functionalities, and energy performance resulting from the VERYSchool project methodology have been demonstrated and validated in four European school pilots. As a whole, the project has achieved excellent results. The entire Energy Management Programme established in each pilot school has been validated in compliance with the ISO 50001 during one year of experimental activities. A methodology for the application of IPMVP in school buildings has been developed, with examples on how to calculate energy savings and comfort conditions. The energy performances assessment, and the achieved energy savings in the project, was performed with both:
- energy indicators calculated for the current year over the previous one, using measured versus and billed data;
- the eeMeasure software, that is provided by the European Commission as a tool to calculate energy savings with a standard methodology. On average, 30% for heating, 12% on lighting dimming control, 70% on LED lights.
The energy and environmental assessment were performed using the Building Energy Index (BEI), the Climate Energy Index (CEI) and the Carbon Assessor (CA), all belonging to the market product IES <Virtual Environment>.. Using the Optimization Scenarios appropriate to each pilot school, a Green Design has been performed as best practices to show how the selected pilot schools can be transformed into Near-Zero Energy Building. The consistent dataset comprising both the experimental data collected and the HQDS data are made for public download to the benefit of the scientific Community at the link fpt:// ………………………. The Catalogue of the Optimization Scenarios, which support the decision-making process of VSNavigator has been published as e-Book and it is free downloadable from the project website. The results of the statistical analysis related to the on-line survey that involved about 2.000 responders, are made as free publication to provide information and create awareness on the actual level of knowledge for implementing an Energy Management System in European.
VERYSchool project has been recognized for the high level of innovation that have introduced, and in 2013 received an Award as best European project within the Green Digital Charter, with ceremony held in Amsterdam during the EUROCITIES conference. VSNavigator is a specific technology and a replicable model. Any reference to the school building, or school organization, automatically extends to the general concept of “building” or “organization”. VSNavigator has been developed with the contribution of European funds as CIP-ICT-PSP project, but it is also the result of a research and innovation action. Thus, the VSNavigator software is not released as a product ready for the market. The Consortium aims to pursue the goal to give value to the efforts and the expenditures made with public money to strengthen the competitiveness and Innovation of the European Industry. Thus, to make the business plan realistic and successful, the Consortium set up an exploitation strategy that considers the “sell of the rights” of the VSNavigator software to Organizations who wish to buy.
Partners¶
AESS (IT) has a core mission in the promotion of renewable energy source and in reduction of energy consumption among Local Authorities, SMEs and consumers. Main activities are related to: - Energy plans, building regulation, promotion of sustainable energy communities; - European projects, training and promotion campaigns concerning energy and environmental initiatives (to specific stakeholders/institutions: schools, companies, public bodies, citizens, etc); - Building energy audit and boiler inspections; - Replacement of fossil fuel sources with renewable sources; - Consultancy for improving local energy systems (Local Authorities, Private companies and citizens); - Energy performance contracting implementation; - Assistance for energy saving in public buildings and lightings.
SCE Group / DOKI (IT) is a group of companies located in Modena, Italy, sharing the same assets and resources through the constitution of an internal Technology Park, a building area of 21.000 m2 in total, where all the companies making part of the group are hosted. SCE was founded in 1978 and started to work in the field of industrial electronics operating in the sector of industrial products and services. Over the years, the company broadened their skills building products for different sectors, thanks to continuous investments in research, development, and expansion of their sales and marketing network. Based on its experience, SCE has become a leading manufacturer of custom electronics, industrial PCs, terminals and CNC Operators. SCE is UNI EN ISO 9001:2008: UNI EN ISO 14001:2004 certified for quality management systems and has obtained the certificate of environmental management system.
The Computer and Automation Research Institute, Hungarian Academy of Sciences (HU) - has gained a worldwide reputation in operations research, computer graphics, computer-aided design and manufacturing, process control, robotics, numerical methods, advanced information systems and networking. An important mission of the Institute is to realise technology transfer to the Hungarian industry and service sectors including SMEs. ERCIM (European Research Consortium of Informatics and Mathematics) granted full membership to SZTAKI in 1994. Many researchers are members of editorial boards of leading international scientific periodicals. The international reputation of the Institute is reflected in its prestigious title of “Centre of Excellence” in information technology, computer science and control given by the EU in 2000. The researchers involved in the project belong to the research Laboratory on Engineering and Management Intelligence, at SZTAKI Main skills of this laboratory refer to research and techniques applicable for handling complex production and business systems working in an uncertain, changing environment, with special emphasis on business-process modelling, re engineering, simulation, production control and scheduling, object oriented software design, internet technologies.
Energy Agency of Plovdiv (EAP, BG) is an expert company promoting efficient and sustainable use of energy and renewable energy. Its services are utilised by the public administration, businesses communities, and consumers. It carries out feasibility studies, energy analyses, energy projects identification, development and management. EAP is the first energy management agency established in Bulgaria under the SAVE II program of the European Commission (EC) in 2000. EAP has developed and managed more than 30 RES and EE energy projects together with national and international partners. The work of EAP is based on a quality management system and a code of ethics that has been signed by the staff, management board and associated experts. They have been working for many years for European projects and clients and at the same time contributing to the development of local energy efficiency and renewable energies solutions of common sense for energy independence and competitive prices. The experts’ profession expertise covers deep energy, economic, and financial analyzing, policy advise, project management, writing and promotion.
Enerit (IRL) develops and supplies “software as a service” (SaaS) for the newly launched energy management standard ISO 50001 – the first company in the world. This product is targeted at large energy users (with energy bills greater than € 1Mio/year) who are: - pursuing ISO 50001 and who have suitable management and technical skills internally; or - employing external energy management consultants to run their energy management function as an out-sourced activity
D’Appolonia S.p.A. (IT) , with its 500 staff, is the largest fully independent Italian engineering firm which provides integrated services to clients belonging both to the public and the private sector in the energy, environment, construction, oil and gas, transport, electronics and telecommunications domains. D’Appolonia relies on a permanent staff of qualified engineers and scientists, mainly based in the headquarters in Genoa, Italy. Most of the staff has an extended academic and technical background with post-graduate degrees. Their skills are related to civil and structural engineering, earth sciences and geotechnical engineering, hydrology and hydraulic engineering, risk, reliability and safety, chemical and process engineering, transportation systems, mechanical engineering, environmental engineering and science, electronics and telecommunications, aerospace and aeronautics. Since its foundation D’Appolonia has participated in more than 20,000 projects worldwide. The firm offers a full range of integrated engineering services to support the Customers in the development of complex projects, covering the early phases of conceptual design and definition of specifications up to implementation, optimization and validation. A multidisciplinary Division provides specialist engineering services in the field of Industrial Innovation, supporting SMEs as well as large companies in the achievements of their targets in product and process innovation. The company’s multidisciplinary problem solving approach is continuously supported by the most advanced technical and scientific developments, where research and innovation play a relevant role.
Genoa Municipality (IT) is a local authority which is experimenting a new method of city government and governance through a creative exercise in steps, with new forms of social co-operation involving the whole community, with the idea of integrating public (local Institutions, all the authority levels) and private sectors for projects of economic, social and environmental transformation scheduled in the period from 2004 (when Genoa was European Capital of Culture) to 2010 and beyond. Genoa Municipality’s objectives are actually focused on education and solidarity, quality of life, economy and employment, communication and promotion of the City, Port and infrastructures, city management improvement. Genoa Municipality aims at improving urban energy efficiency in order to enhance City’s profile in line with Energy Action Plan recently approved by Genoa in the framework of the European Covenant of Mayors. Genoa has a strong experience in the project-related subjects. Some of the key initiatives and projects are: - Requalification of historical urban parks with funds from Columbus funds and regional POR funds. In particular the parks: Nervi, historical Aqueduct, Villa Duchessa di Galliera and Villa Pallavicini - Green plan with maintenance of Valletta Rio Sanpietro (reconstruction of natural ecosystem and terraces) with European funds - Preparation of Action Plan within the Covenant of Mayors initiative with energy diagnosis and identification of actions to reach, within 2020, a 20% reduction of CO2 emissions and at least 20% of energy produced by renewable sources and energy saving.
Energia Propria (PT) is the first ESCO (Energy Service Company) of the Portuguese and of the Iberian market, that promotes pioneering combination of the energy efficiency in buildings with decentralized energy and micro-generation implementation utilizing renewable energies. Self Energy provides integrated and complete energy management solutions and services that maximize the value of energetic resources and proposes energy cost reduction contracts based on performance supported by certified energy audits and by the installation of equipment with private or public funding. The combination of the best international manufacturers of micro-generation and renewable technologies, with the most conceited European universities in the sector, ensures the continuous implementation of innovative technologies applied to suit the customers need.
Integrated Environmental Solutions (IES, UK) is developer of the world’s leading integrated building performance modelling software system the <Virtual Environment>. As such IES have unsurpassed experience in the application of these advanced design tools to enhance building performance, and create more sustainable buildings. Founded in 1994, employing 87 staff, and headquartered in Glasgow (Scotland) with offices in London (England), Dublin (Ireland), Cambridge (MA), San Francisco (CA), Melbourne (Australia), Pune (India) and Penang (Malaysia). In this time IES has provided leading edge support to the design, construction and operation of some of the largest and most challenging buildings in the world. IES’s international Consulting arm works side-by-side with building design teams to provide detailed simulation analysis and develop a range of innovative solutions. IES acts as an educator by training and accrediting customers, and working with students and academic institutions to support teaching of performance analysis as part of sustainable architecture and engineering courses.
University of Belgrade – Faculty of Mechanical Engineer (UBFME, RS) provides university level education in the mechanical engineering profession in Serbia. UBFME is the first faculty which successfully completed the accreditation process in Serbia. UBFME performs research and education in twenty one specialised research areas. The Faculty has large capacities in terms of the number of researchers, laboratories and research projects. More than 3000 students are currently studying at the faculty and about 400 of them graduate each year. It is also active as an institution that is leading and participating in a number of national projects. At the present moment, the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering is trying to improve its participation in regional and European projects as well. During recent years the main EC Projects have been: - HERD Energy project Sustainable Energy and Environment in the Western Balkans, 2010-2014 - International Accreditation of Engineering Studies , 144856-TEMPUS-2008-RS-JPGR - PubTrans4All – Public transportation – Accessibility for all (PUBTRANS4ALL) Funded under 7th FWP (Seventh Framework Programme) - TransNew Support for realising New Member and Associated States’ potentials in transport research Project FP7-TPT-2008.8-RTD-1 – 234330 TransNEW
Ankara National Education Directorate (TR) is the second biggest local public authority involved in education across 81 Provinces in Turkey. It is responsible for the planning, coordination and management of all kinds of educational and training activities for pre-school, primary, secondary, vocational and technical and adult education in 25 districts of Ankara. The institution has a range of duties mainly in 7 fields: management, personnel education and training, budget and investment, research, planning and statistics, inspection, guidance and investigation and civil engineering. These duties are carried out by 24 affiliated units. Under its management there are 1569 schools. Furthermore AMEM work directly together with Turkey Education Ministry supporting it on policy and regulation development, impacting directly on all 700000 schools in Turkey. AMEM has a strong experience in the project-related subjects. Some of the key initiatives and projects are: - Development and implementation of LdV Transfer of Innovation Project, “ENERTEACH: development of further training modules in the fields of energy efficient construction and renewable energy applications in buildings” - Development and implementation of World Bank Project, “Training of technical teachers in the field of renewable energy technologies” - Pilot Energy Efficiency Implementations in 6 different schools